A report by Arcane Research and Luno shows a growing relevance of crypto-currencies in Africa. The demand for crypto assets on the continent is driven by a young population, frequent currency crises and a lack of payment infrastructure.
The states of Nigeria, South Africa and Ghana are therefore all represented in the TOP 5 for search queries on “Bitcoin” from the last twelve months. Google Trends is an online service provided by the company Google LLC, which provides information on which search terms are searched for by users of the search engine and how often. The results are set in relation to total search volume and have been available in weekly resolution globally, or for individual regions, since the beginning of 2004. With the help of Google Trends, the popularity of individual terms can be analyzed over time, allowing conclusions to be drawn about emerging trends in society. Often the price of Bitcoin correlates with the search volume in Google Trends.
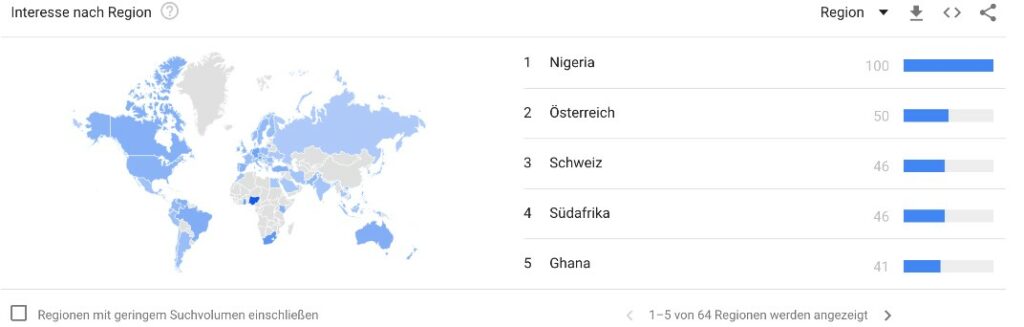
Nigeria has recently been dominant for a long time in terms of the volume of trade in crypto-currencies on the African continent. This is usually done via P2P markets. Recently, however, the country has been replaced by South Africa. The proportion of people who own crypto-currencies in South Africa is thus around 13 percent, with Nigeria coming in second in Africa (11 percent).
Great potential for crypto-currencies in Africa
Although the continent has major infrastructure deficiencies, the African continent has great potential for crypto-currencies. The report argues that the region is optimal for crypto assets, as Africa has a young population and is often hit by currency crises. The continent is home to around 1.27 billion people, or about 17% of the world’s population. Africa’s population is significantly younger than the global average and is growing much faster. Africa’s median average age is 18 years, while 97% of the Sub-Saharan population is under 65 years of age.
The majority of African countries suffer from high inflation rates, which robs citizens of wealth and purchasing power. Bitcoin and other crypto currencies with disinflationary money models offer some protection against currency devaluation. Inflation rates throughout Africa have historically been well above the global average. Extreme examples such as the hyperinflation in Zimbabwe bear witness to such developments.
But political uncertainties and a deficient payment infrastructure also favour the adaptation of crypto-currencies. The fragility of national politics and unstable government structures, forced migration and the confiscation of assets are commonplace in Africa. Bitcoin and other crypto-currencies can serve as value preservers which, combined with attributes such as censorship resistance, can provide an antidote to political chaos.
The trading volume on the peer-to-peer Bitcoin marketplace “Localbitcoins” has been rising sharply recently. Last week, South Africa recorded the second largest weekly volume. Around 1.65 million US dollars changed hands in the form of Bitcoin.
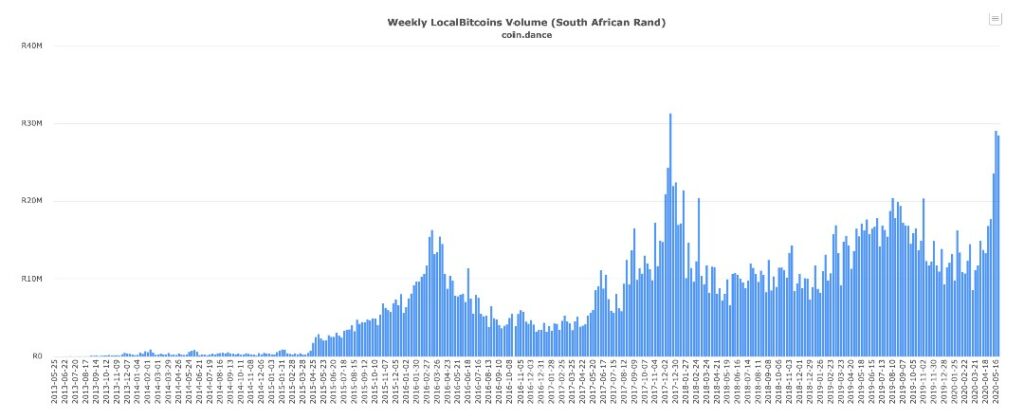
Apart from South Africa, P2P trade in African countries has been increasing in general in the recent past. Kenya, Nigeria and Egypt have also seen record trading activity in recent weeks.
Regulatory hurdles in Africa
The most hostile countries to crypto-currencies are Algeria, Libya, Morocco and a few others, all of which have issued a ban on the use of crypto-currencies. Kenya, Ghana, Swaziland, Uganda, Zambia and Zimbabwe are monitoring the use of crypto-currencies but have not actively banned it. In countries such as Namibia or Burundi there are no prohibitions on use, but there are trade bans. The reasons for bans are manifold. Most often, the high volatility, fraud in connection with crypto-currencies and lack of regulatory guidelines are cited.